Why Do We Use Alternating Current (AC) Electricity?
What is Alternating Current (AC) Electricity?
Alternating Current (AC) is a type of electrical current in which the flow of electric charge periodically reverses direction. AC is the form of electricity that is delivered to businesses and residences and is used by most household appliances and devices. AC electricity is favored over Direct Current (DC) for its efficiency in transmitting over long distances and its ability to be easily converted to different voltages.
When you use electricity at home, you might not think about its type, source, or functionality. While it may not be the most thrilling subject, understanding the difference between Alternating Current (AC) and Direct Current (DC) electricity is crucial. Let’s dive into the basics of AC electricity and why it is the standard for power distribution today.
The History of Electricity
Electricity wasn’t invented by a single person; it’s a natural phenomenon. Static electricity, like the shock from touching certain objects, has been known for centuries. The journey to harnessing electricity involved many inventors and scientists.
In the 18th century, Benjamin Franklin demonstrated the electrical nature of lightning through his famous experiment. Thomas Edison, renowned for practical electric lighting systems, patented the commercially viable incandescent lightbulb, crucial for widespread electric lighting adoption. However, it wasn’t just Edison; other inventors like Nikola Tesla and George Westinghouse significantly advanced electrical technology.
The Advent of Direct Current Electricity
Thomas Edison’s practical electric lighting set the stage for electricity generation and distribution, initially using Direct Current (DC). DC was predominant for about two decades. However, Nikola Tesla’s advocacy for Alternating Current (AC) marked a turning point. Tesla invented the AC induction motor, proving AC’s efficiency for long-distance transmission and its adaptability to different voltage levels.
By 1896, AC electricity was established as the preferred choice for homes and businesses, thanks to Tesla’s innovations and contributions from other inventors.
AC vs. DC: Understanding the Difference
Alternating Current (AC) electricity flows back and forth, unlike Direct Current (DC) electricity, which flows in one direction. AC’s ability to travel longer distances efficiently and transform into different voltage levels made it the standard for widespread use. AC is also easier and safer to work with, essential for home applications.
The Benefits of AC Electricity
- Transmission Efficiency: AC can be transmitted over long distances with minimal power loss, thanks to its ability to step up voltage using transformers. High-voltage transmission reduces energy loss, making it cost-effective for powering distant areas.
- Voltage Transformation: AC’s ability to be easily transformed to different voltage levels is crucial for efficient power distribution. High voltage is used for transmission, while lower voltage is safer for household use.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The infrastructure for AC electricity, including transformers and power lines, is well-established and cost-efficient. This makes AC more economical for large-scale power distribution.
- Safety: AC is safer for domestic use due to its lower voltage levels in households. The ability to cut off power in cycles reduces the risk of severe electric shocks compared to DC.
- Compatibility with Modern Devices: Most household appliances and electronics are designed to run on AC power. The widespread adoption of AC ensures compatibility with a variety of devices.
- Flexibility and Reliability: AC systems can handle higher power loads and are more robust in dealing with power surges, making them reliable for both residential and industrial applications.
AC Electricity in Modern Times
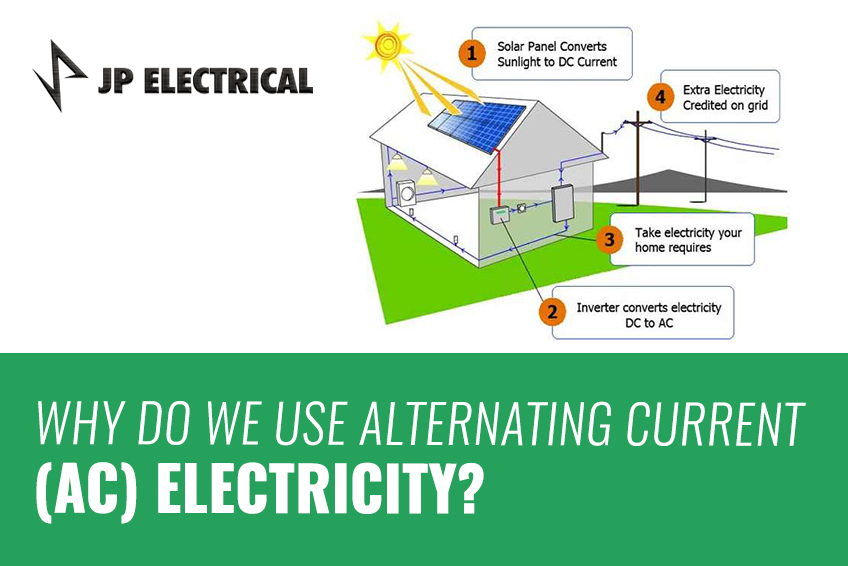
Today, we continue to use AC electricity for most residential and commercial needs, while DC electricity powers specific low-current applications like car batteries and portable solar systems. Modern solar panels produce DC power, converted to AC via transformers for compatibility with home and business use.
Call JP Electrical for All Your Electricity Needs
We’re lucky to have such a manageable way to power our homes and devices! However, that doesn’t mean it’s safe or that anyone can do electrical work if a problem arises. That’s where JP Electrical’s professional electricians come in handy. It’s important to schedule a professional to make any changes or maintain your electrical systems within your home or business.
For more information on our services, visit our residential services and commercial services pages. You can also learn more about the history and benefits of AC electricity from this article by the U.S. Department of Energy.
We can handle any job you have, and we always ensure we’ve done an excellent job. Give us a call today!
Categories: Electrical Maintenance • Energy Efficient